Online Medical Care



On January 28, 2022, the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare partially revised the “Guidelines for the Appropriate Implementation of Online Medical Treatment” published in March 2018, and organized three terms related to telemedicine.
Each term is divided into two categories, one involving a physician’s judgment and the other not, so it is important to understand the content.
To begin, we will discuss the three terms that define online medical care.
*The “Guidelines for the Appropriate Implementation of Online Medical Treatment” were partially revised on March 30, 2023.
(1) Online medical practice
Online medical care refers to the act of examining and diagnosing a patient in real time between a physician and a patient using information and communication devices.
Online medical services also include the transmission of diagnostic results and prescribing of medications.
(2) Online medical consultation recommendation
Online medical consultation recommendation refers to the act of recommending a patient to visit a medical institution after a real-time consultation between a physician and a patient using information and telecommunications equipment.
Based on the patient’s complaints and symptoms, the doctor determines the suspected disease, selects the appropriate department to be consulted, and makes the minimum necessary medical judgment based on the patient’s physical and mental condition.
It is also possible to recommend a patient for follow-up observation including home treatment using OTC drugs or a non-visit to a doctor.
However, communication of treatment methods or specific instructions for the use of pharmaceuticals by citing specific disease names constitutes online medical treatment and must not be performed within the scope of recommending a medical examination.
(3) Telehealth medical consultation
Telemedicine consultations are divided into those conducted by physicians and those conducted by non-physicians.
Telemedicine consultation by a physician refers to the act of providing necessary medical advice based on information obtained through the use of information and communication devices, according to the mental and physical condition of the individual patient.
Specific decisions such as medical examinations and diagnoses based on the patient’s condition are not made, and only advice is provided.
However, if a person other than a physician is consulted, the consultation is limited to the provision of general medical information and recommendations for medical consultation. They cannot make medical judgments such as presenting the possibility of disease or diagnosis based on the patient’s condition.
Diabetes Mellitus
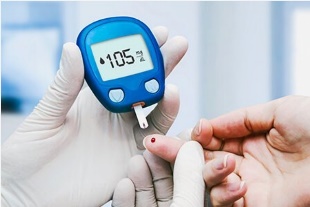
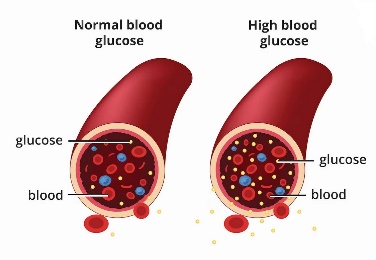
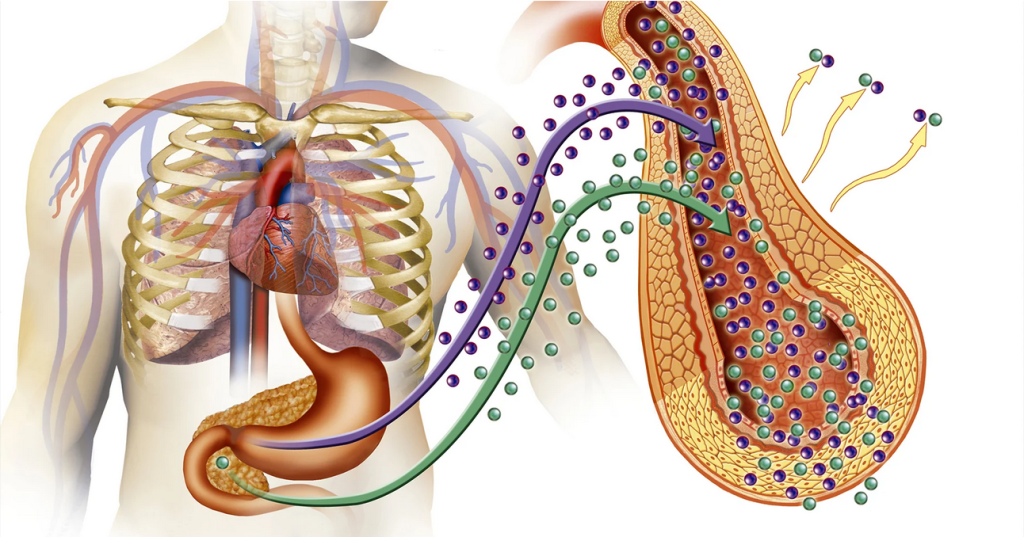
Diabetes mellitus is a disease in which insulin does not work adequately, causing an increase in the amount of sugar called glucose (blood sugar) flowing through the blood. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas and is responsible for keeping blood sugar within a certain range.
If blood sugar levels (blood glucose) remain high for years, blood vessels can become damaged, leading to more serious diseases (chronic complications of diabetes) such as heart disease, blindness, kidney failure, and amputation in the future. In addition, extremely high blood glucose levels by themselves can cause coma (acute complication of diabetes).
Hypertension

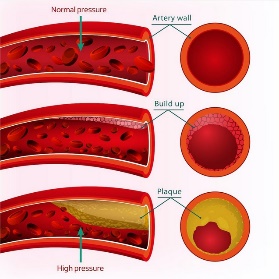

Hypertension is a condition of high blood pressure. When blood pressure is measured by chance and is high, it can be said to be high, but it cannot be called “hypertension. Hypertension is when blood pressure is higher than normal even after repeated measurements. Hypertension is diagnosed when the maximum blood pressure is 140 mmHg or higher or the minimum blood pressure is 90 mmHg or higher in repeated measurements in the examination room.